Ex7: The Skin & Other Body Membranes
Refer to the Lab worksheet : https://sites.google.com/site/physiolablist/
There are several sections to this lab, generally designed to assist students in understanding the structures & functions of skin & other body membranes. The objectives of this lab are:
- to recount important functions of the skin/integumentary system
- to recognize and name the following structures from a slide, model or diagram
- epidermis (including strata),
- dermis (papillary & reticular layers
- hair follicles & hair
- sebaceous glands & sweat glands
- to compare the properties of the dermis & epidermis
- to describe the distribution and function of the sebaceous glands, sweat glands, and hair
- to differentiate between eccrine & apocrine sweat glands
- to ennumerate the factors determining skin color
- to describe the function of melanin
- to compare the structure and function of the major membrane types
- to list the general functions of each membrane type and note its location in the body
- to recognize by microscopic examination epidermal, mucous, and serous membranes
II. Hypothesis
Part 1: Basic structure of the skin: If students read about structures as they locate them on a skin model then they will be able to write out a response to each objectivePart 2: Appendages of the Skin: If students examine a prepared slide of human skin then they will be able to identify skin structures on a drawing.
Part 3: Plotting the Distribution of sweat glands: If bond paper is taped to skin coated with iodine and left for 20 minutes, then a distribution of sweat glands will be mapped out because the sweat glands will dissolve the iodine, which will then be absorbed by the paper. As it reacts with the starch in the bond paper each sweat gland will produce a blue/black dot.
Part 4: Classification of Membranes: If students examine slides from trachea and small intestine, heart, as well as a freshly cut joint, then they can compare mucous, serous and synovial membranes.
III. Materials
Model of Skin, prepared slides/pictures, iodine, 1cm x 1 cm bond paper squares, tape.
IV. Procedure
“See Lab Instructions” (you may include pictures of procedure)
Part 1: Basic structure of the skin: Compare the following structures identified in the pictures with the model in the classroom. |
| Skin slide |
 |
| Human Skin Slide |
Part 3: Plotting the Distribution of sweat glands: Insert a photo of each of your sweat distribution patches. Label them "palm" and "forearm".
palm forearm
Part 4: Classification of Membranes:
 |
| pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium |
 |
| mucosa of trachea |
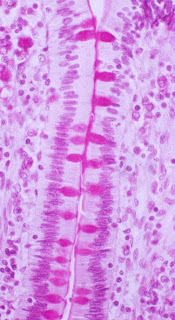 | |||
| mucosa of small intestine |
 |
| drawing of one villus |
 | |
| pericardium (around the heart) |
V. Results/Observation/Data
List answers to questions from each section of the lab
Part 1: Basic structure of the skin: (No questions in this section)List answers to questions from each section of the lab
Part 2: Appendages of the Skin:
wider view of the skin than the slides we used
Part i3: Plotting the Distribution of sweat glands:
the palm
Labeled Pictures:
Part 4: Classification of Membranes:
small intestine is being used absorb while trachea is used to capture and move out of your body
yes because they have a bunch of nutrients around them
The pericardium is an example of a serous membrane. It's too tiny to see, but the endothelium is composed of simple squamous epithelium. List the specific names of the following serous membranes:
covering of the heart:
Lining of the cavity in which the heart resides:
Covering of the lungs:
Lining of the thoracic cavity:
Covering on the viscera:
Lining of the visceral cavity:
small intestine is being used absorb while trachea is used to capture and move out of your body
yes because they have a bunch of nutrients around them
The pericardium is an example of a serous membrane. It's too tiny to see, but the endothelium is composed of simple squamous epithelium. List the specific names of the following serous membranes:
covering of the heart:
Lining of the cavity in which the heart resides:
Covering of the lungs:
Lining of the thoracic cavity:
Covering on the viscera:
Lining of the visceral cavity:
VI. Conclusion: Respond to each objective. What did you learn?
- What are the important functions of the skin/integumentary system?
- Can you recognize and name the following structures from a slide, model or diagram?
- epidermis (including strata),
- dermis (papillary & reticular layers
- hair follicles & hair
- sebaceous glands & sweat glands
- Compare the properties of the dermis & epidermis
- Describe the distribution and function of the sebaceous glands, sweat glands, and hair
- Differentiate between eccrine & apocrine sweat glands
- Ennumerate the factors determining skin color
- Describe the function of melanin
- Compare the structure and function of the major membrane types
- List the general functions of each membrane type and note its location in the body
- Can you recognize by microscopic examination epidermal, mucous, and serous membranes?


